Can We Do Anything About Climate Change
This content is more than 2 years old
Climate science tin be circuitous, and misinformation in politics and the media can make information technology difficult to sort fact from fiction. Hither, we've answered eight common climate change questions, including what'south causing climate change, what scientists are saying and what nosotros can do nigh information technology. Read on to become up to speed!
1. What is climate alter?
two. What is causing climate change?
3. How is climate modify affecting Australia?
4. Why practise just a few degrees of warming matter?
5. How do scientists know the climate is changing?
6. What are the main sources of greenhouse gas emissions in Commonwealth of australia?
seven. What can Australia do to combat climate change?
viii. How does Commonwealth of australia measure upwards on the world stage?
ix. Where can I observe out more than?
1. What is climate change?
Climate is unlike from weather condition. When nosotros talk about the Earth's climate, we are referring to the average atmospheric condition conditions over a period of 30 years or longer. Weather, on the other hand, refers to what you see and experience outside from 24-hour interval to day (e.g. sunny, rainy).
So climate change is whatsoever change in the climate, lasting for several decades or longer, including changes in temperature, rainfall or wind patterns.
The best scientific testify nosotros accept shows that our world is quickly heating.
Long-term air and bounding main temperature records clearly testify the Earth is warming. The global average temperature has already risen past one.ane°C since the time earlier the Industrial Revolution. This might not audio similar a lot, merely ane.1°C represents a massive amount of extra heat and energy – the equivalent of four Hiroshima flop detonations per 2d.
While the globe's climate has changed throughout history, scientists concur that the meaning changes nosotros've seen over the past hundred years or and so have been due to human activities. Recent warming is as well happening at a rate that is much faster than previous climatic changes.
Temperature Anomalies past Land 1880-2017 based on NASA GISTEMP data. Past Antti Lipponen.
ii. What is causing climate modify?
The brusque respond is: the excessive corporeality of greenhouse gases inbound the World'southward atmosphere due to human activeness is causing our climate to heat dramatically. Merely at that place'south more to it than that.
Let'southward break information technology down. A certain amount of greenhouse gases (similar water vapour, ozone, carbon dioxide, marsh gas and nitrous dioxide) occur naturally. For example, carbon dioxide is produced through the respiration of natural ecosystems (plants), or through the decay of organic matter (biomass). These greenhouse gases human activity like a blanket in our atmosphere, trapping some of the dominicus'due south heat close to the Earth's surface. This is known equally the 'greenhouse effect' – and it makes the planet warm enough for us to live.
But since the Industrial Revolution (which began in the mid to late 1700s), greenhouse gases accept built up in the temper, leading to more heat being trapped close to the earth'due south surface. This is considering Western civilisations began digging up and called-for coal, oil and gas on a massive scale. At the same time, agriculture, tree-immigration (deforestation) and the production of waste (landfill) also increased. All of these processes also produce greenhouse gases.
As more greenhouse gases are added to the Earth'southward atmosphere, more of the sun's heat is trapped. This causes the Earth's average temperature to rise.
Carbon dioxide is the most pregnant of all the greenhouse gases, followed past methyl hydride. Carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere have increased past more than 45% since the Industrial Revolution and are now the highest they have been for at least 800,000 years.
iii. How is climatic change affecting Australia?
Australia is one of the almost vulnerable developed countries in the world to the impacts of climate change. These include:
- Increased frequency and/or severity of extreme weather events including floods and droughts. Read more here .
- More frequent, more than intense and longer-lasting heatwaves. Heatwaves are deadly, having killed more than people than all other extreme weather events in Australia combined. Read more hither .
- Greater hazard and severity of bushfires and earlier, longer bushfire seasons. Read more here .
- Sea level rise, leading to more coastal flooding, erosion and saltwater intrusion into freshwater wetlands, such as in the World-Heritage listed Kakadu National Park. Low-lying backdrop most rivers and coastlines are likewise at adventure posing significant threats to commercial, industrial, road, rail, and residential assets. Read more here .
- Impacts on wildlife due to heat stress, drought and habitat changes, which have menstruum-on effects downwards the nutrient concatenation. Commonwealth of australia holds the showtime record of a mammalian extinction due to climatic change. Read more hither .
- More frequent marine heatwaves, which bear on marine ecosystems such as the Great Bulwark Reef. After the back-to-dorsum marine heatwaves in 2016 and 2017, fifty% of the coral on the Great Barrier Reef died. Mass bleaching occurred again in 2020. Read more here .
- Impacts on health due to changes in air pollution and air-borne allergens (such as pollen), vector-borne diseases, extreme weather events and other factors. Read more than hither .
- Increased pressure on emergency services and wellness systems, equally the fire seasons of states and territories increasingly overlap which stretches resource, and the health impacts of climatic change worsen. Read more than here .
- Agronomical impacts from more frequent droughts, floods and heatwaves. Read more hither .
Nosotros are already experiencing these impacts today, at a rise in temperature of just 1.1 ̊C since the pre-industrial flow. In recent times, Australia has been rocked by the Black Summer of 2019-2020 characterised by catastrophic bushfires, unprecedented in their scale and impairment; has seen devastating floods in Townsville; and a fierce drought which threatened the food and water security of Australians for many years.
The risks to our wellbeing and livelihoods, and to other species and ecosystems, become much more than profound as temperatures continue to rise.
Read more about droughts, bushfires and other extreme weather condition events in Commonwealth of australia here.
4. Why do but a few degrees of warming matter?
A few degrees of warming is incredibly significant.
The piece of work of the Intergovernmental Console on Climatic change (IPCC) shows the dire consequences nosotros face up if we fail to limit the global temperature increase to one.5°C. Even at one.1°C of global warming, how much the global temperature has increased by so far, the impacts we accept seen from a changing climate accept been intolerable. Lives, livelihoods and homes have been unnecessarily destroyed and communities are under abiding pressure. It is essential that nosotros do our best to hold global temperatures equally depression as possible, as shown in the following infographic.

Adjusted from WRI (07/x/18) based on data from IPCC (10/2018).
To avoid the impacts we'd experience at 2 degrees warming, we have no other choice only to limit our warming as close to one.5 ̊C equally possible.
If nothing changes, we could exist on track for a rise in temperatures of betwixt 4-6 ̊C. To put this in context, the difference in temperatures between now and the terminal ice age was around 4 ̊C.
The Paris Agreement is a global treaty agreed to past over 190 countries around the globe. In this agreement, the global customs committed to limit global warming to well beneath 2°C and to pursue efforts to limit warming to 1.five ̊C. Information technology is an of import step towards addressing the global claiming of climatic change. But with the electric current pledges that countries have put forward, the world is on rails for at least 3.2 ̊C of warming past the stop of the century.
v. How practice scientists know the climate is changing?
Scientists collect data about the climate by testing a number of things: air and ocean temperature, precipitation, sea level, ocean salinity and acidity, tree rings, marine sediments, and pollen, to proper name a few.
Water ice cores from Antarctica are incredibly helpful in showing how the climate has changed over fourth dimension, because they tin can provide a tape of what the level of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and marsh gas were in our atmosphere in the past, too as providing clues nigh past temperatures. Water ice core information stretches dorsum 800,000 years and shows that the concentration of greenhouse gases in our atmosphere over this period has never increased so quickly, or by so much, as information technology has during recent times.
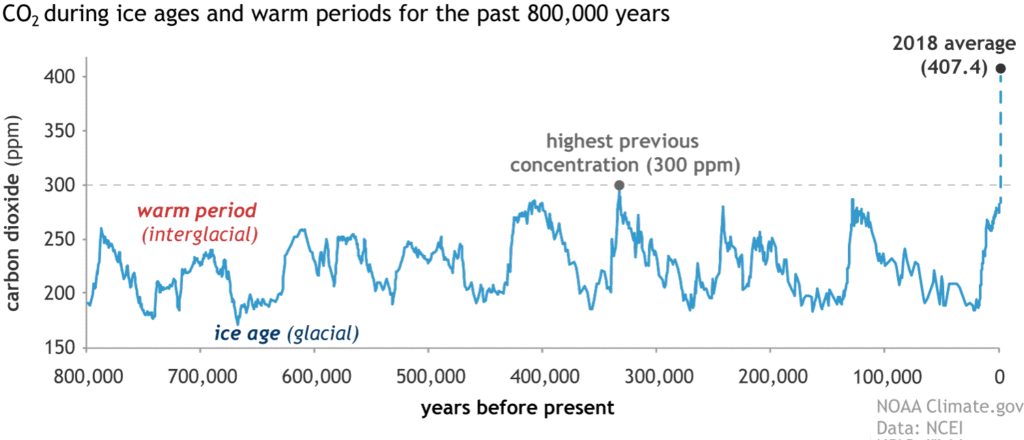
Carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere over the past 800,000 years, based off data from water ice cores. C02 levels accept never been equally loftier as they are at present. Source: NOAA
Pulling all of this data together, scientists have concluded that humans have been driving the significant changes in climate that nosotros are currently experiencing. The bear witness that supports anthropogenic (homo-caused) climate change is vast and includes many lines of evidence published in tens of thousands of peer-reviewed periodical articles.
6. What are the main sources of greenhouse gas emissions in Australia?
At that place are viii major areas (sectors) in Australia responsible for our greenhouse gas emissions:
- Electricity (emissions from burning coal and gas to ability our lights, appliances and more)
- Send (emissions from petrol and diesel used to power cars, trucks and buses, and emissions from aviation fuel used to power planes)
- Stationary energy (fuels like gas consumed directly, rather than used for electricity, in industry and in households)
- Agronomics (greenhouse gases such every bit methane and nitrous oxide produced by animals, manure management, fertilisers and field called-for)
- Avoiding emissions (gases vented from fossil fuel extraction and transportation)
- Industrial processes (emissions produced by converting raw materials into metallic, mineral and chemical products)
- Waste product (emissions from decaying organic matter)
- State use, state use alter and forestry (LULUCF) (emissions and removals mainly from forests, just also from croplands, grasslands, wetlands and other lands).
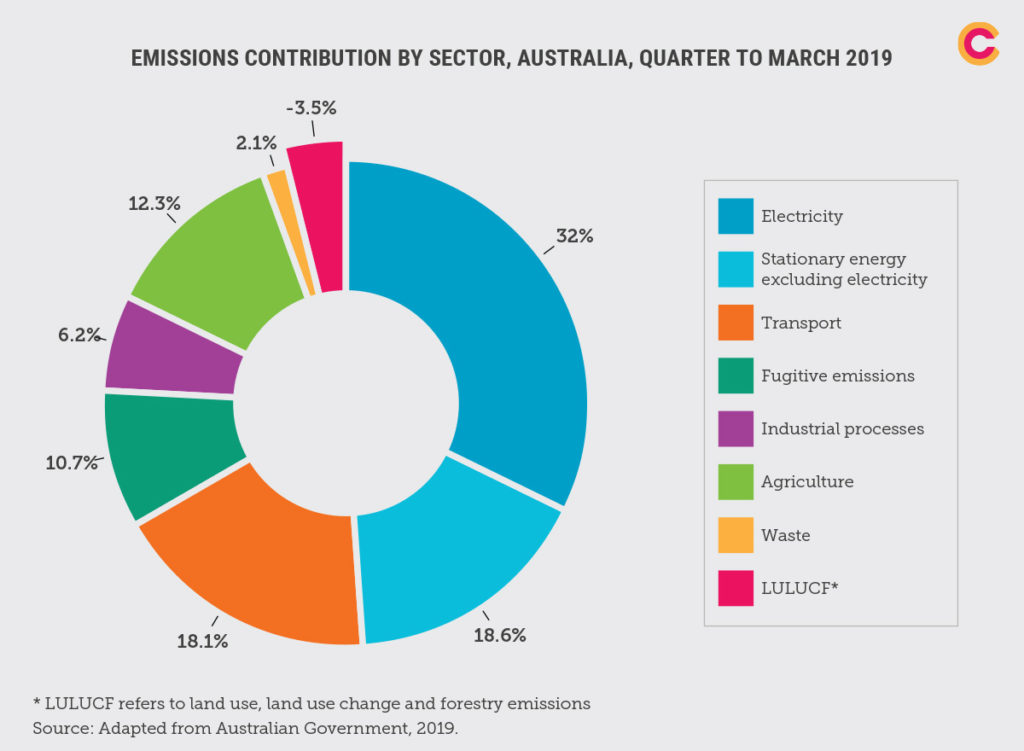
Australia'south greenhouse gas emissions by sector, 2019. Electricity remains the biggest contributor of greenhouse gases in Australia. Source: March 2019 quarterly updates.
Electricity is the largest source of greenhouse gas emissions in Commonwealth of australia, responsible for 32% of emissions. This is mainly because 84% of our electricity comes from called-for fossil fuels, the large bulk of this (59.9%) is from called-for coal.
Fortunately, Commonwealth of australia is the sunniest and one of the windiest countries in the world, which means nosotros are perfectly placed to generate our electricity from renewable energy sources, like solar and wind.
Updating Commonwealth of australia'southward energy system with renewables and storage is crucial for cut our greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change.
vii. What can Australia exercise to combat climate alter?
Although we are already experiencing the consequences of climate change today, we too have the solutions to address it.
Australia urgently needs to reduce its greenhouse gas emissions every bit role of a strong global effort.
In 2018, the IPCC ended that the world must cut emissions to internet zero past no afterwards than 2050 to have a chance of limiting warming to 1.five ̊C. This meant that global carbon dioxide emissions would need to be roughly halved by 2030. Since 2018 our understanding has grown still further, and it is at present articulate that even faster action is necessary to meet the goals of the Paris Agreement. Put simply, emissions need to collapse this decade and attain net cypher past 2040 at latest.
Here are the easiest, most efficient and cost-constructive ways for Commonwealth of australia to reduce its greenhouse gas emissions:
- Electricity
Rapidly transitioning away from fossil fuel generated electricity to renewable energy and storage technologies is the quickest and cheapest style to reduce emissions. In Australia and many other countries, new renewable free energy is at present cheaper than new coal and global investment in coal has plummeted by 75% in three years. - Transport
Fugitive unsafe climate change doesn't start and end with irresolute electricity. Nosotros also need to electrify our transport systems – similar buses, cars, trains and trams – and ability them with 100% renewable electricity also. Ship makes upwards around 19% of Australia'southward greenhouse gas emissions, but these emissions can exist reduced by: improving public transport'due south quality, efficiency and accessibility, encouraging active send (such as cycling and walking), and building infrastructure (like vehicle charging stations), to encourage people to use electric vehicles. - Agriculture
Agriculture contributes roughly 13% of Australia's emissions, and deforestation accounts for around 9% of Australia's emissions. Simply climate solutions like reforestation and regenerative agriculture can increase how much carbon is stored in soils and vegetation, removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. - Fossil fuels
Australia needs to actively transition away from fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas, including those we consign. Every bit the second largest exporter of both thermal coal (which is burned to generate electricity) and gas, Australia has a huge influence on global emissions and the fossil fuel market. If nosotros include all the fossil fuels that Australia exports, Commonwealth of australia is the fifth biggest polluter in the world – so we're a big deal when it comes to climate change.Commonwealth of australia should not corroborate any new fossil fuel projects, and must actively phase out existing projects to reduce emissions. This process has to support fossil fuel-dependent communities and workers – and brand sure that they take opportunities to move into other industries.
eight. How does Australia measure upward on the globe stage?
Australia is a very big deal on the earth stage when it comes to causing climatic change.
In 2019, Australia was the worlds' largest liquefied fossil gas exporter, the globe's 2d largest coal exporter.
Combined with our very high emissions at home, Australia packs a big dial to the global climate. Even ignoring its exported fossil fuels, Australia is the 14th biggest greenhouse polluter in the world. There are 195 countries signed up to the Paris Agreement. More than 180 countries of them emit less than Australia per yr, and this list includes several of the world's largest economies, and many countries with far larger populations. This includes the birthplace of the Industrial Revolution: the United kingdom.
Alongside all of this, Australia has routinely played a central office in hobbling international climate negotiations over the entire life of international climate diplomacy, and this continues right up until today.
This is all important because, while the whole world needs to meet a net nil goal by 2050, countries like Australia, that accept been major causes of our supercharged global climate, must reduce far sooner if in that location is whatever hope of achieving globally agreed temperature goals.
For this goal to be achievable, Australia must drive down all emissions, beyond all sectors at present.
Electric current levels of Regime inaction on climate change cannot continue. There is no more time for piecemeal and token efforts to reduce emissions on one manus while at the aforementioned time overseeing desperate increases elsewhere.
9. Where can I observe out more?
The Climate Council has created a range of scientific discipline-backed materials to further explain the causes, impacts and solutions to climate alter. Take a wait at our Reports, Videos and Infographics.
These might also involvement you:
What tin can Yous do to tackle climate change?
Watt's watt? A guide to renewable energy chapters and generation
Climate Action: 6 reasons to feel inspired not defeated
Let's Get Something Direct – Australia Is Not On Rails To Meet Its Paris Climate Target
Deforestation and Climate change
How climatic change is damaging Australia'southward economy
Source: https://www.climatecouncil.org.au/resources/what-is-climate-change-what-can-we-do/
Posted by: parkfrommory.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Can We Do Anything About Climate Change"
Post a Comment